Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Effective properties of a cubic material
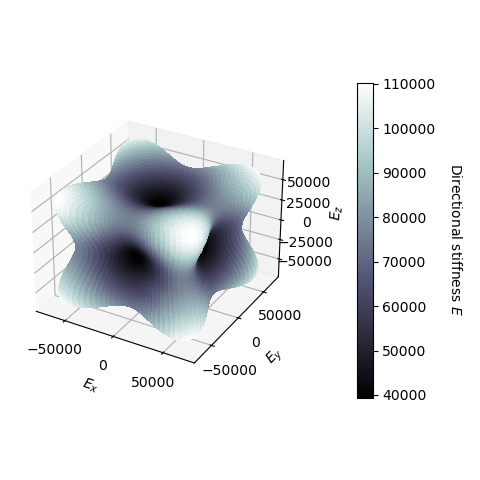
This tutorial studies the directional stiffness of a cubic material
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm, colors
import simcoon as sim
import os
Define a grid of directions in 3D space using spherical coordinates (θ, φ) and compute the components of the unit vector n.
phi = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 128) # azimuthal angle in the xy-plane
theta = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 128).reshape(128, 1) # polar angle
n_1 = np.sin(theta) * np.cos(phi)
n_2 = np.sin(theta) * np.sin(phi)
n_3 = np.cos(theta) * np.ones(128)
n = (
np.array([n_1 * n_1, n_2 * n_2, n_3 * n_3, n_1 * n_2, n_1 * n_3, n_2 * n_3])
.transpose(1, 2, 0)
.reshape(128, 128, 1, 6)
)
Use Simcoon to obtain the cubic stiffness matrix L and its inverse (compliance M).
C11 = 185000.0
C12 = 158000.0
C44 = 39700.0
L = sim.L_cubic([C11, C12, C44], "Cii")
M = np.linalg.inv(L)
Compute the directional stiffness E(n) = 1 / (nᵀ·M·n) for all directions.
S = (n @ M @ n.reshape(128, 128, 6, 1)).reshape(128, 128)
E = 1.0 / S
x = E * n_1
y = E * n_2
z = E * n_3
Plot the directional stiffness as a 3D surface.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(1))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection="3d")
norm = colors.Normalize(vmin=np.min(E), vmax=np.max(E), clip=False)
surf = ax.plot_surface(
x,
y,
z,
rstride=1,
cstride=1,
norm=norm,
facecolors=cm.bone(norm(E)),
linewidth=0,
antialiased=False,
shade=False,
)
ax.set_xlabel(r"$E_x$")
ax.set_ylabel(r"$E_y$")
ax.set_zlabel(r"$E_z$")
scalarmap = cm.ScalarMappable(cmap=plt.cm.bone, norm=norm)
cbar = fig.colorbar(scalarmap, ax=ax, shrink=0.7, pad=0.15)
cbar.set_label(r"Directional stiffness $E$", rotation=270, labelpad=20)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.473 seconds)